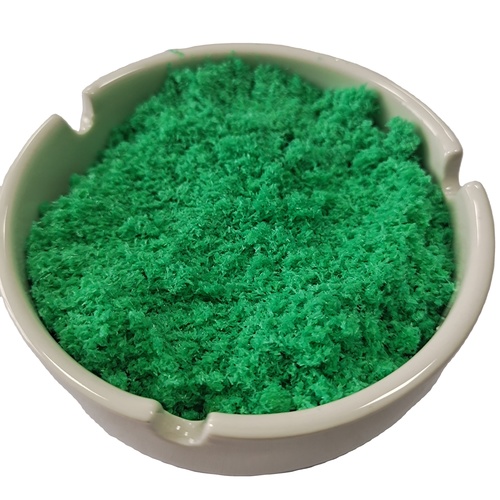

cuprous chloride
Product Details:
- Shape Powder
- Molecular Formula CuCl
- Taste Odorless
- Structural Formula ClCu
- Melting Point 430 C
- Storage Store in a tightly closed container, keep away from moisture and light
- Other Names Copper(I) chloride
- Click to View more
cuprous chloride Product Specifications
- Powder
- CuCl
- ClCu
- Odorless
- 10125-13-0
- Cuprous chloride
- cuprous chloride
- Inorganic chemical
- 233-040-8
- Complies with industrial specifications
- Inorganic compound
- Copper(I) chloride
- Store in a tightly closed container, keep away from moisture and light
- 430 C
- Technical Grade
- Used in pigments, catalysts, dyes, and as an analytical reagent
- Odorless
- Yes
- 99%
- 98.99 g/mol
- Insoluble in water, soluble in NH4OH and concentrated hydrochloric acid
- Solid
- Releases HCl on heating; decomposes before boiling
- Industrial, laboratory
- 28273990
- 4.14 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Harmful if swallowed, may cause irritation
- Available in 25 kg HDPE bags
- Stable under recommended storage
- Ionic compound
- Crystalline powder
- <0.005%
- <0.5%
- Compatible with most solvents except oxidizing agents
- Fine powder
- White to pale green
- 2 years
cuprous chloride Trade Information
- 100 Per Month
- 3 Days
Product Description
Quick Details
Classification:
CHLORIDE
Type:
copper chloride dihydrate
CAS No.:
10125-13-0
Other Names:
Cupric Chloride
MF:
Cucl2 2H2OQuick Details
Classification:
CHLORIDE
Type:
copper chloride dihydrate
CAS No.:
10125-13-0
Other Names:
Cupric Chloride
MF:
Cucl2 2H2O
Place of Origin:
Zhejiang,China
Grade Standard:
Industrial Grade
Purity:
98
Appearance:
crystal
Application:
colorant/catalyst/Plating additive
Brand Name:
Hongsheng
Product Name:
Cupric Chloride
Packing:
25kg
Grade:
Industrial Grade Agriculture Grade
Color:
Blue-green
Storage:
Dry Place
Sample:
Supplied
MOQ:
500KG
Shape:
Crystalline Granule
Product class:
Dangerous Chemicals
Main components:
Cucl2 2H2O
Grade Standard:
Industrial Grade
Purity:
98
Appearance:
crystal
Application:
colorant/catalyst/Plating additive
Product Name:
Cupric Chloride
Packing:
25kg
Grade:
Industrial Grade Agriculture Grade
Color:
Blue-green
Storage:
Dry Place
Sample:
Supplied
MOQ:
500KG
Shape:
Crystalline Granule
Product class:
Dangerous Chemicals
Main components:
Cucl2 2H2O
Product Features and Specifications
Cuprous chloride is available as a fine powder with a moisture content below 0.5% and a lead content lower than 0.005%. It is packed in 25 kg HDPE bags, complying with industrial safety and quality standards. With a melting point of 430C, it is best kept in tightly closed containers away from moisture and light to maintain its stability and shelf life of 2 years.
Applications and Compatibility
This inorganic compound is widely utilized in the manufacturing of pigments, dyes, and catalysts, as well as serving as an analytical reagent in laboratories. Its ionic nature makes it compatible with most solvents except oxidizing agents. Cuprous chlorides insolubility in water and solubility in ammonium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid further broaden its industrial utility.
FAQs of cuprous chloride:
Q: How should cuprous chloride be stored to ensure its stability?
A: Cuprous chloride should be kept in a tightly closed container, stored away from moisture and light, to maintain its stability and quality throughout its shelf life.Q: What are the main applications of cuprous chloride?
A: Cuprous chloride is primarily used as a pigment, catalyst, dye, and analytical reagent in industrial and laboratory settings due to its chemical properties and stability.Q: When does cuprous chloride begin to decompose, and what precautions should be taken during heating?
A: Cuprous chloride decomposes before boiling, releasing hydrogen chloride (HCl) upon heating. Proper ventilation and handling with appropriate protective equipment are advised to prevent exposure to hazardous fumes.Q: Where can cuprous chloride be sourced, and in what packaging is it supplied?
A: This compound is manufactured, exported, and supplied in India, typically available in 25 kg HDPE bags designed for safe storage and transport.Q: What is the compatibility of cuprous chloride with solvents, and which ones should be avoided?
A: Cuprous chloride is compatible with most solvents, but contact with oxidizing agents should be avoided to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.Q: How is cuprous chloride beneficial in industrial processes?
A: Its high purity, fine particle size, and stability make cuprous chloride valuable in industrial processes that require precise chemical performance, especially in pigments and catalysis.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Industrial Chemical' category








 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free
